Functions Palette/Programming/Boolean: Difference between revisions
Add new page |
m Rename category to "Functions Palette" |
||
| Line 438: | Line 438: | ||
* [[Boolean]] | * [[Boolean]] | ||
[[Category: | [[Category:Functions Palette]] | ||
Revision as of 17:39, 21 July 2019
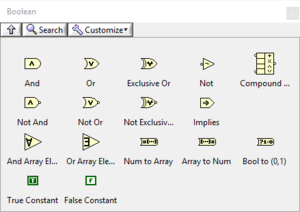
The Boolean palette provides constants and functions that can be performed on Boolean, Numeric and Fixed-point values.
Logical And
Accepts two Boolean or numeric inputs.
Boolean: If provided Boolean values, returns ![]() if both inputs are
if both inputs are ![]() , otherwise returns
, otherwise returns ![]() .
.
| x | y | output |
|---|---|---|
Numeric: If provided numeric values, performs a bit-wise AND operation.
| Binary | Decimal | |
|---|---|---|
| x | 10101010
|
170 |
| y | 11110000
|
240 |
| output | 10100000
|
160 |
Logical Or
Accepts two Boolean or numeric inputs.
Boolean: If provided Boolean values, returns ![]() if any input is
if any input is ![]() , otherwise returns
, otherwise returns ![]() .
.
| x | y | output |
|---|---|---|
Numeric: If provided numeric values, performs a bit-wise OR operation.
| Binary | Decimal | |
|---|---|---|
| x | 10101010
|
170 |
| y | 11110000
|
240 |
| output | 11111010
|
250 |
Exclusive Or
Accepts two Boolean or numeric inputs.
Boolean: If provided Boolean values, returns ![]() if any input is
if any input is ![]() exclusively, otherwise returns
exclusively, otherwise returns ![]() .
.
| x | y | output |
|---|---|---|
Numeric: If provided numeric values, performs a bit-wise XOR operation.
| Binary | Decimal | |
|---|---|---|
| x | 10101010
|
170 |
| y | 11110000
|
240 |
| output | 01011010
|
90 |
Not
Returns the inverted value of an Boolean or numeric input.
Boolean:
| x | output |
|---|---|
Numeric:
| Binary | Decimal | |
|---|---|---|
| x | 10101010
|
170 |
| output | 01010101
|
-171 |
Compound Arithmetic
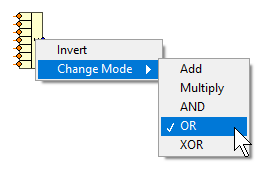
Performs various logical and arithmetic operations on Boolean and numeric values for a dynamic amount of inputs.
Available operations:
- Add
- Multiply
- AND (see Logical And)
- OR (see Logical Or)
- XOR (see Exclusive Or)
This function is especially useful when doing logical and arithmetic operations on more than two input values.
Invert input and output:
The Compound Arithmetic function allows to invert any of the inputs as well as the output selectively.
Not And
This is the same as Logical And but the output is inverted.
Boolean:
| x | y | output |
|---|---|---|
Numeric
| Binary | Decimal | |
|---|---|---|
| x | 10101010
|
170 |
| y | 11110000
|
240 |
| output | 01011111
|
95 |
Not Or
This is the same as Logical Or but the output is inverted.
Boolean:
| x | y | output |
|---|---|---|
Numeric:
| Binary | Decimal | |
|---|---|---|
| x | 10101010
|
170 |
| y | 11110000
|
240 |
| output | 00000101
|
5 |
Not Exclusive Or
This is the same as Exclusive Or but with inverted output.
Boolean:
| x | y | output |
|---|---|---|
Numeric:
| Binary | Decimal | |
|---|---|---|
| x | 10101010
|
170 |
| y | 11110000
|
240 |
| output | 10100101
|
165 |
Implies
Accepts two Boolean or numeric inputs.
Boolean: If provided Boolean values, returns ![]() if the first input is
if the first input is ![]() and the second input is
and the second input is ![]() . Otherwise returns
. Otherwise returns ![]() .
.
| x | y | output |
|---|---|---|
Numeric: If provided numeric values performs a bit-wise implies operation.
| Binary | Decimal | |
|---|---|---|
| x | 10101010
|
170 |
| y | 11110000
|
240 |
| output | 11110101
|
-11 |
And Array Elements
Performs the Logical And on an n-dimensional array of Boolean values. This means, the output is ![]() if all elements of the array are
if all elements of the array are ![]() . Note that this function works an multi-dimensional arrays, not just one-dimensional.
. Note that this function works an multi-dimensional arrays, not just one-dimensional.
Or Array Elements
Performs the Logical Or on an n-dimensional array of Boolean values. This means, the output is ![]() if any element of the array is
if any element of the array is ![]() . Note that this function works an multi-dimensional arrays, not just one-dimensional.
. Note that this function works an multi-dimensional arrays, not just one-dimensional.
Num to Array
Converts an integer or fixed-point number to a Boolean array. The size of the output array depends on the size of the provided number. Note that the least significant bit is at index zero.
Array to Num
Converts a Boolean array to an integer or fixed-point number with the least significant bit at index zero.
Bool to (0,1)
Returns a Boolean into a 16-bit integer.
| x | output |
|---|---|
| 0 | |
| 1 |
True Constant
This is the Boolean True constant ![]()
False Constant
This is the Boolean False constant ![]()