Case structure: Difference between revisions
→Introduction: Update and extend |
Update and restructure |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ | {{Underconstruction}} | ||
[[File:Case Structure - Components.png|thumb|Components of a Case Structure]] | |||
A Case Structure is a primitive [[Functions Palette/Programming/Structures|Structure]] that can have multiple [[Subdiagram|Subdiagrams]] (also known as "Cases"), one of which is selectively executed at runtime. A selector value determines which case is executed at runtime. The Structure autmatically adapts to the [[:Category:Data types|data type]] connected to the Case selector and must have exactly one Subdiagram for each possible value of the connected data type, or a ''Default'' case to handle undefined values. | |||
== Supported data types == | |||
The Case Structure automatically adapts to following data types: | |||
* [[Boolean|Boolean]] | |||
* [[Integer|Integer]] | |||
* [[Enum|Enum]] | |||
* [[String|String]] | |||
* [[Error Cluster|Error Cluster]] | |||
Some features are only available for specific data types. | |||
<br clear="all"> | |||
== Boolean Case Structure == | |||
== | |||
[[File:Case Structure - Boolean.png|thumb|Case Structure with Boolean value]] | |||
The Boolean Case Structure is the default Structure when placed from the [[Functions Palette]]. It has exactly two cases: ''True'' and ''False''. | |||
=== | <br clear="all"> | ||
== Integer Case Structure == | |||
[[File:Case Structure - Integer.png|thumb|Case Structure with Integer value]] | |||
[[ | The Integer Case Structure uses an [[Integer]] as selector value and can have as many cases as the specific Integer type supports. | ||
Non-integer values ([[Fixed-point]], [[Single Precision]], [[Double Precision]], [[Extended Precision]]) are [[Rounding|rounded]] according to [[wikipedia:IEEE 754-1985|IEEE 754-1985]]. | |||
Complex numbers ([[Complex Single]], [[Complex Double]], [[Complex Extended]]) are not supported and will break the VI. | |||
=== | === Tricks === | ||
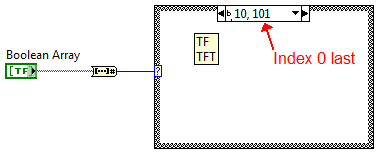
==== Range selector ==== | |||
Integer cases can have ranges. These ranges can be open ''(3..)'' or closed ''(3..10)''. Multiple ranges can be connected by a comma ''(3..10, 12..)''. | |||
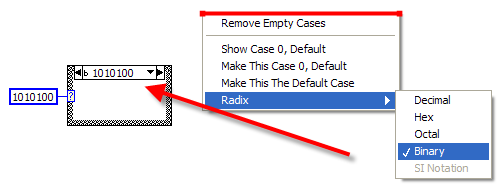
==== Radix ==== | |||
It is possible to change the number representation between ''Decimal'', ''Hex'', ''Octal'' and ''Binary''. To change the representation, simply right-click on the selector label and select ''Radix''. | |||
[[Image:Example of radix in case structure.png]] | [[Image:Example of radix in case structure.png]] | ||
[[Image:BinaryCaseSelect.png]] | [[Image:BinaryCaseSelect.png]] | ||
|} | |||
=== Enum | <br clear="all"> | ||
== Enum Case Structure == | |||
[[File:Case Structure - Enum.png|thumb|Case Structure with Enum value]] | |||
The [[Enum]] case structure uses the string interpretation of the value to label the cases. | The [[Enum]] case structure uses the string interpretation of the value to label the cases. | ||
=== Tricks === | |||
* To have a case for every Enum value right click on the selector label of the case structure and select ''add case for every value''. | |||
* Don't add a ''Default'' case, if the Enum datatype changes the code will break and you'll be triggered that a case should be added. | |||
* A Tab-control's datatype is an Enum as well, so it's possible to connect a tab control directly to a case structure. | |||
<br clear="all"> | |||
== String Case Structure == | |||
[[File:Case Structure - String.png|thumb|Case Structure with String value]] | |||
The string case structure uses the string value to select which case should execute. | The string case structure uses the string value to select which case should execute. | ||
=== Tricks === | |||
* Selection is by default done ''case sensitive'', to make the selection ''case insensitive'' right click on the selector label and select ''Case insensitive match'' | |||
* A default case is obliged | |||
* Ranges | |||
Just like integer and Enum case structures a string case structure accepts ranges. To detect all string starting with foo the following range would apply <tt>"foo".."foo~"</tt>. By adding the tilde on the end of the range you will get all strings starting with <tt>foo</tt> up to <tt>foo~</tt>. The <tt>tilde</tt> is the last visible ASCII character. | |||
==== Caveats for using ranges ==== | |||
*The range of <tt>"UI:".."UI:Z"</tt> is not inclusive of <tt>"UI:Z"</tt>. To be inclusive you need to explicitly add it like this: <tt>"UI:".."UI:Z", "UI:Z"</tt> -- see [http://zone.ni.com/reference/en-XX/help/371361E-01/lvhowto/creating_case_structs/ docs] for details. Using <tt>tilde</tt> will not match the value with the <tt>tilde</tt> | *The range of <tt>"UI:".."UI:Z"</tt> is not inclusive of <tt>"UI:Z"</tt>. To be inclusive you need to explicitly add it like this: <tt>"UI:".."UI:Z", "UI:Z"</tt> -- see [http://zone.ni.com/reference/en-XX/help/371361E-01/lvhowto/creating_case_structs/ docs] for details. Using <tt>tilde</tt> will not match the value with the <tt>tilde</tt> | ||
| Line 83: | Line 81: | ||
*String range matches are case sensitive (even if your case structure is configured for Case Insensitive Match, I believe), so you'd want to use a range like <tt>"UI:".."UI:zzzzzzzzzzzzzz"</tt>, since <tt>"z"</tt> (0x7A) > <tt>"Z"</tt> (0x5A) -- see [http://zone.ni.com/reference/en-XX/help/371361E-01/lvhowto/creating_case_structs/ docs] for details.<br> | *String range matches are case sensitive (even if your case structure is configured for Case Insensitive Match, I believe), so you'd want to use a range like <tt>"UI:".."UI:zzzzzzzzzzzzzz"</tt>, since <tt>"z"</tt> (0x7A) > <tt>"Z"</tt> (0x5A) -- see [http://zone.ni.com/reference/en-XX/help/371361E-01/lvhowto/creating_case_structs/ docs] for details.<br> | ||
=== Error | <br clear="all"> | ||
== Error Case Structure == | |||
[[File:Case Structure - Error Cluster.png|thumb|Case Structure with Error Cluster]] | |||
The [[Error Case Structure|error case structure]] is like the boolean case structure but can be controlled by the <tt>error state</tt> of an [[Error cluster]]. The border of the <tt>error case</tt> is red and the <tt>non-error case</tt> is green. | The [[Error Case Structure|error case structure]] is like the boolean case structure but can be controlled by the <tt>error state</tt> of an [[Error cluster]]. The border of the <tt>error case</tt> is red and the <tt>non-error case</tt> is green. | ||
[[ | <br clear="all"> | ||
== General Items == | |||
On compile time the compiler assures that at least one case will run when the code executes, if this cannot be determined the containing VI will be [[Broken]]. To provide a case for values of the selector that is general a case can be labeled ''Default''. One case can be used to handle several selector values. To enter these provide a <tt>,</tt> (comma) between the values. A range of these values can be set by providing <tt>..</tt> (two dots) between the values. | |||
== Editing tips and tricks == | |||
*To create a new case after the current case use <tt><shift-enter></tt>, to duplicate the current case to a new case use <tt><ctrl-shift-enter></tt> | |||
*You can right click on the selecter and sort or switch cases | |||
[[Category:Case Structure]] | |||
[[Category:Structures]] | [[Category:Structures]] | ||
Revision as of 18:34, 24 July 2019
 |
This page is under construction. This page or section is currently in the middle of an expansion or major revamping. However, you are welcome to assist in its construction by editing it as well. Please view the edit history should you wish to contact the person who placed this template. If this article has not been edited in several days please remove this template. Please don't delete this page unless the page hasn't been edited in several days. While actively editing, consider adding {{inuse}} to reduce edit conflicts. |
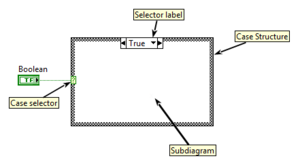
A Case Structure is a primitive Structure that can have multiple Subdiagrams (also known as "Cases"), one of which is selectively executed at runtime. A selector value determines which case is executed at runtime. The Structure autmatically adapts to the data type connected to the Case selector and must have exactly one Subdiagram for each possible value of the connected data type, or a Default case to handle undefined values.
Supported data types
The Case Structure automatically adapts to following data types:
Some features are only available for specific data types.
Boolean Case Structure
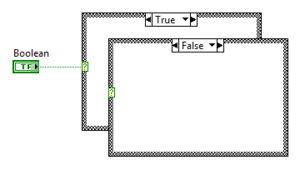
The Boolean Case Structure is the default Structure when placed from the Functions Palette. It has exactly two cases: True and False.
Integer Case Structure
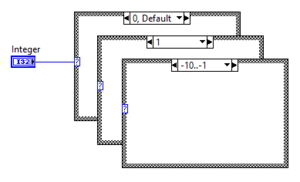
The Integer Case Structure uses an Integer as selector value and can have as many cases as the specific Integer type supports. Non-integer values (Fixed-point, Single Precision, Double Precision, Extended Precision) are rounded according to IEEE 754-1985. Complex numbers (Complex Single, Complex Double, Complex Extended) are not supported and will break the VI.
Tricks
Range selector
Integer cases can have ranges. These ranges can be open (3..) or closed (3..10). Multiple ranges can be connected by a comma (3..10, 12..).
Radix
It is possible to change the number representation between Decimal, Hex, Octal and Binary. To change the representation, simply right-click on the selector label and select Radix.
Enum Case Structure
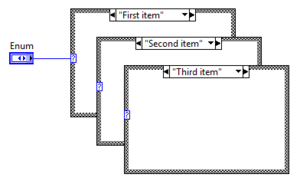
The Enum case structure uses the string interpretation of the value to label the cases.
Tricks
- To have a case for every Enum value right click on the selector label of the case structure and select add case for every value.
- Don't add a Default case, if the Enum datatype changes the code will break and you'll be triggered that a case should be added.
- A Tab-control's datatype is an Enum as well, so it's possible to connect a tab control directly to a case structure.
String Case Structure
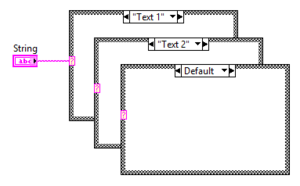
The string case structure uses the string value to select which case should execute.
Tricks
- Selection is by default done case sensitive, to make the selection case insensitive right click on the selector label and select Case insensitive match
- A default case is obliged
- Ranges
Just like integer and Enum case structures a string case structure accepts ranges. To detect all string starting with foo the following range would apply "foo".."foo~". By adding the tilde on the end of the range you will get all strings starting with foo up to foo~. The tilde is the last visible ASCII character.
Caveats for using ranges
- The range of "UI:".."UI:Z" is not inclusive of "UI:Z". To be inclusive you need to explicitly add it like this: "UI:".."UI:Z", "UI:Z" -- see docs for details. Using tilde will not match the value with the tilde
- If you wanted to include frames like "UI: Zoom Out" (that have more characters than just UI: Z), then you'd probably want to set your range to something like "UI:".."UI:zzzzzzzzzzzzz" (Note: I used lowercase "z" on purpose -- see next point) or the tilde.
- String range matches are case sensitive (even if your case structure is configured for Case Insensitive Match, I believe), so you'd want to use a range like "UI:".."UI:zzzzzzzzzzzzzz", since "z" (0x7A) > "Z" (0x5A) -- see docs for details.
Error Case Structure
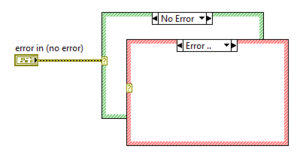
The error case structure is like the boolean case structure but can be controlled by the error state of an Error cluster. The border of the error case is red and the non-error case is green.
General Items
On compile time the compiler assures that at least one case will run when the code executes, if this cannot be determined the containing VI will be Broken. To provide a case for values of the selector that is general a case can be labeled Default. One case can be used to handle several selector values. To enter these provide a , (comma) between the values. A range of these values can be set by providing .. (two dots) between the values.
Editing tips and tricks
- To create a new case after the current case use <shift-enter>, to duplicate the current case to a new case use <ctrl-shift-enter>
- You can right click on the selecter and sort or switch cases