Mercurial: Difference between revisions
m merge-tools section |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[Image:Logo.Mercurial.png|left]]{{TOCright}}<br> | [[Image:Logo.Mercurial.png|left]]{{TOCright}}<br> | ||
Mercurial is a [[Source Code Control|Source Code Control]] system by Selenic, it's key feature is the distributed nature of the system.<br> | Mercurial is a [[Source Code Control|Source Code Control]] system by Selenic, it's key feature is the distributed nature of the system.<br> | ||
This means that changes (commits) are stored in a local repository, which can be sent (pushed) to a central repository and which can be downloaded (pulled) by others.<br> | This means that changes (commits) are stored in a local repository, which can be sent (pushed) to a central repository and which can be downloaded (pulled) by others.<br> | ||
= Getting started<br> = | = Getting started<br> = | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
= Configuration<br> = | = Configuration<br> = | ||
Mercurial stores it's setting in a file called 'hgrc' inside a hidden folder '.hg'<br> | Mercurial stores it's setting in a file called 'hgrc' inside a hidden folder '.hg'<br> | ||
== Setting up LVMerge<br> == | == Setting up LVMerge<br> == | ||
[http://zone.ni.com/reference/en-XX/help/371361F-01/lvhowto/configmerge_thirdparty/ LVMerge] can be used by Mercurial as a Merge tool. Add the following text to the hgrc file:<br> | [http://zone.ni.com/reference/en-XX/help/371361F-01/lvhowto/configmerge_thirdparty/ LVMerge] can be used by Mercurial as a Merge tool. Add the following text to the hgrc file:<br> | ||
<pre>[merge-tools] | <pre>[merge-tools] | ||
LVMerge.args = $base $other $local $output | LVMerge.args = $base $other $local $output | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
**.xctl = LVMerge | **.xctl = LVMerge | ||
**.lvlib =LVMerge | **.lvlib =LVMerge | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
== Setting up LVDiff<br> == | == Setting up LVDiff<br> == | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
=== Configure<br> === | === Configure<br> === | ||
To be able to select lvdiff as the diff tool you need to add teh follwoing settings to the [merge-tools] section of the hgrc configuration file:<br> | To be able to select lvdiff as the diff tool you need to add teh follwoing settings to the [merge-tools] section of the hgrc configuration file:<br> | ||
<pre>lvdiff.diffargs = $child $parent | <pre>lvdiff.diffargs = $child $parent | ||
lvdiff.executable =C:\Program Files\lvdiff\lvdiff.exe | lvdiff.executable =C:\Program Files\lvdiff\lvdiff.exe | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
lvdiff.binary = True | lvdiff.binary = True | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
If you are using TortoiseHg 1.0.1 or later, you can add a [diff-patterns] section (analogous to merge-patterns above,) enabling automatic selection of the visual diff tool: | |||
<pre> | |||
[diff-patterns] | |||
**.vi = lvdiff | |||
**.ctl = lvdiff | |||
**.lvclass = lvdiff | |||
**.xctl = lvdiff | |||
**.lvlib = lvdiff | |||
</pre> | |||
=== Start LVDiff<br> === | === Start LVDiff<br> === | ||
| Line 71: | Line 82: | ||
== Ignoring files<br> == | == Ignoring files<br> == | ||
Mercurial stores general ignore patterns in a file called '.hgignore' in the repository root, so you can add the patterns to the repository. I use the following patterns<br> | Mercurial stores general ignore patterns in a file called '.hgignore' in the repository root, so you can add the patterns to the repository. I use the following patterns<br> | ||
<pre>.ogp$ | <pre>.ogp$ | ||
/built*$ | /built*$ | ||
| Line 81: | Line 92: | ||
= Performing a merge<br> = | = Performing a merge<br> = | ||
The following conditions needs to be true to be able to perform a merge:<br> | The following conditions needs to be true to be able to perform a merge:<br> | ||
*All local changes needs to be commited (hg st should only show ?)<br> | *All local changes needs to be commited (hg st should only show ?)<br> | ||
*A changeset is pushed by another user to the central repository<br> | *A changeset is pushed by another user to the central repository<br> | ||
*The other changeset is not yet pulled<br> | *The other changeset is not yet pulled<br> | ||
The merge will try to detect the differences and call LVMerge if necesarry, LVmerge will show four VIs:<br> | The merge will try to detect the differences and call LVMerge if necesarry, LVmerge will show four VIs:<br> | ||
*Base, the base VI which was present in the changeset that is the same on both repositories<br> | *Base, the base VI which was present in the changeset that is the same on both repositories<br> | ||
*Mine, local commited VI<br> | *Mine, local commited VI<br> | ||
*Their, remote VI with edits from the other user<br> | *Their, remote VI with edits from the other user<br> | ||
These are not editable.<br> | These are not editable.<br> | ||
*Resulting, this is the VI that will be stored to disc after the merge finalizes. This file can be edited by the user<br> | *Resulting, this is the VI that will be stored to disc after the merge finalizes. This file can be edited by the user<br> | ||
For each diff LVMerge will give options to use either, 'base', 'mine' or 'their' code.<br> | For each diff LVMerge will give options to use either, 'base', 'mine' or 'their' code.<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
After the merge the code should be committed and pushed.<br> | After the merge the code should be committed and pushed.<br> | ||
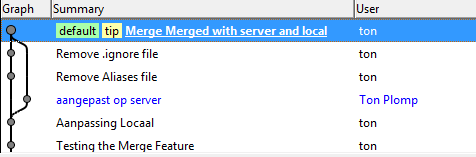
Most Mercurial Clients will show a graph with the following layout:<br> | Most Mercurial Clients will show a graph with the following layout:<br> | ||
[[Image:MergeTrackHG.png|border]]<br> | [[Image:MergeTrackHG.png|border]]<br> | ||
Here's the same graph from the 'other' user, which actually performed the merge: | Here's the same graph from the 'other' user, which actually performed the merge: | ||
| Line 115: | Line 126: | ||
= Mercurial clients = | = Mercurial clients = | ||
On Windows[[Image:Logo.Windows.png]], Mac[[Image:Logo.Mac.png]] and Linux [[Image:Logo.Linux.png]], there is a command line client called 'hg'. On windows there is a context menu tool called [http://tortoisehg.bitbucket.org TortoiseHG] based on the popular TortoiseSVN and TortoiseCVS tools | On Windows[[Image:Logo.Windows.png]], Mac[[Image:Logo.Mac.png]] and Linux [[Image:Logo.Linux.png]], there is a command line client called 'hg'. On windows there is a context menu tool called [http://tortoisehg.bitbucket.org TortoiseHG] based on the popular TortoiseSVN and TortoiseCVS tools | ||
= Further reading = | = Further reading = | ||
| Line 125: | Line 136: | ||
*[http://kiln.stackexchange.com Kiln / Mercurial Knowledge site]<br> | *[http://kiln.stackexchange.com Kiln / Mercurial Knowledge site]<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
[[Category:SCC]] | [[Category:SCC]] | ||
Revision as of 22:09, 14 May 2010
Introduction

Mercurial is a Source Code Control system by Selenic, it's key feature is the distributed nature of the system.
This means that changes (commits) are stored in a local repository, which can be sent (pushed) to a central repository and which can be downloaded (pulled) by others.
Getting started
Joel Spolsky has written a How-To and Why-To page called HG init (hg is the chemical symbol for Mercury).
Configuration
Mercurial stores it's setting in a file called 'hgrc' inside a hidden folder '.hg'
Setting up LVMerge
LVMerge can be used by Mercurial as a Merge tool. Add the following text to the hgrc file:
[merge-tools] LVMerge.args = $base $other $local $output LVMerge.executable = C:\Program Files\National Instruments\Shared\LabVIEW Merge\LVMerge.exe LVMerge.gui = True LVMerge.binary = True [merge-patterns] **.vi = LVMerge **.ctl = LVMerge **.lvclass = LVMerge **.xctl = LVMerge **.lvlib =LVMerge
Setting up LVDiff
LVDiff is a software package that uses the built in diff-functionality from LabVIEW to do command line based LVDiffs.
Download
First thing is to download LVDiff, copy the contents of the zip-file to a location where you have writing priviliges (lvdiff uses a local ini file).
Adjust
Then you need to open up the lvdiff.vi and implement the following changes:
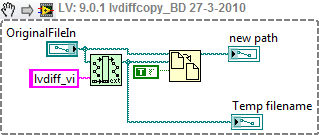
This snippet tests if the filenames are the same and if that's the case it calls a VI called lvdiffcopy, which creates a copy of the file2.
Here's the actual code inside lvdiff copy:
Configure
To be able to select lvdiff as the diff tool you need to add teh follwoing settings to the [merge-tools] section of the hgrc configuration file:
lvdiff.diffargs = $child $parent lvdiff.executable =C:\Program Files\lvdiff\lvdiff.exe lvdiff.gui = True lvdiff.binary = True
If you are using TortoiseHg 1.0.1 or later, you can add a [diff-patterns] section (analogous to merge-patterns above,) enabling automatic selection of the visual diff tool:
[diff-patterns] **.vi = lvdiff **.ctl = lvdiff **.lvclass = lvdiff **.xctl = lvdiff **.lvlib = lvdiff
Start LVDiff
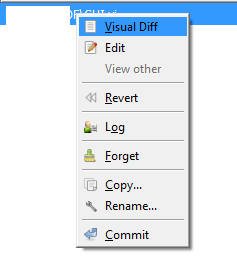
You can start lvdiff in TorsoiseHg in the 'commit' dialog with right-click and 'Visual Diff':
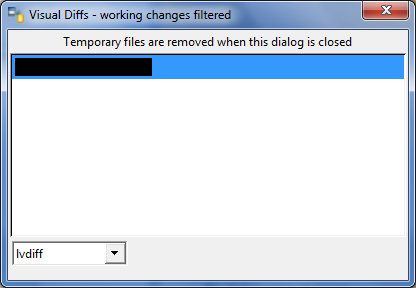
In the following dialog, select 'LVDiff' and double click on the VI to diff:
After this LVdiff will launch LabVIEW and both VI (current and committed) will be compared.
Ignoring files
Mercurial stores general ignore patterns in a file called '.hgignore' in the repository root, so you can add the patterns to the repository. I use the following patterns
.ogp$ /built*$ /build*$ .lvlps$ .aliases$
Performing a merge
The following conditions needs to be true to be able to perform a merge:
- All local changes needs to be commited (hg st should only show ?)
- A changeset is pushed by another user to the central repository
- The other changeset is not yet pulled
The merge will try to detect the differences and call LVMerge if necesarry, LVmerge will show four VIs:
- Base, the base VI which was present in the changeset that is the same on both repositories
- Mine, local commited VI
- Their, remote VI with edits from the other user
These are not editable.
- Resulting, this is the VI that will be stored to disc after the merge finalizes. This file can be edited by the user
For each diff LVMerge will give options to use either, 'base', 'mine' or 'their' code.
After the merge the code should be committed and pushed.
Most Mercurial Clients will show a graph with the following layout:
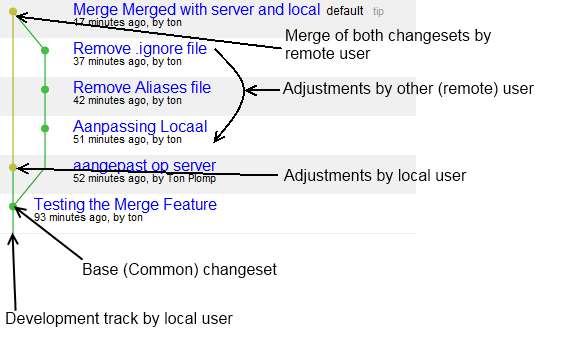
Here's the same graph from the 'other' user, which actually performed the merge:
Here you see the opposite actions, two changesets in the local repo and one in the remote. Only difference is the moment of branching.
Mercurial clients
On Windows![]() , Mac
, Mac![]() and Linux
and Linux ![]() , there is a command line client called 'hg'. On windows there is a context menu tool called TortoiseHG based on the popular TortoiseSVN and TortoiseCVS tools
, there is a command line client called 'hg'. On windows there is a context menu tool called TortoiseHG based on the popular TortoiseSVN and TortoiseCVS tools
Further reading
- Official website
- HG Init
- Mercurial: The Definitive Guide
- Setting Up Mercurial with Apache
- Kiln / Mercurial Knowledge site