Event structure: Difference between revisions
m Q moved page Functions Palette/Programming/Structures/Event Structure to Event structure: Renaming to make it more in line with other palette items. |
Added info table. |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TOCright}} | |||
{{LabVIEW Palette Object Information|palette=Functions Palette/Programming/Structures{{!}}Structures palette|palette2=Functions Palette/Programming/Dialog & User Interface/Events{{!}}Events palette|type=structure}} | |||
[[File:Event Structure - Components.png|thumb|Components of the Event Structure]] | [[File:Event Structure - Components.png|thumb|Components of the Event Structure]] | ||
An Event Structure is a primitive [[Functions Palette/Programming/Structures|structure]] that can have multiple [[Subdiagram|subdiagrams]] (also known as "Event cases"), one of which is selectively executed at runtime. The structure waits for an event to occur, or until the timeout elapsed. While it waits, it doesn't take up any CPU time. Events can be triggered by user input or programmatically by the software. If an event happens while another event is executing, the new event is put on the [[#The event queue|event queue]]. | An '''Event Structure''' is a primitive [[Functions Palette/Programming/Structures|structure]] that can have multiple [[Subdiagram|subdiagrams]] (also known as "Event cases"), one of which is selectively executed at runtime. The structure waits for an event to occur, or until the timeout elapsed. While it waits, it doesn't take up any CPU time. Events can be triggered by user input or programmatically by the software. If an event happens while another event is executing, the new event is put on the [[#The event queue|event queue]]. | ||
== Usage == | |||
== The event queue == | === The event queue === | ||
Each event structure has an event queue that is managed by LabVIEW. The event queue is processed sequentially by the event structure. It is possible to remove elements from the event queue, using the [[Functions Palette/Programming/Dialog & User Interface/Events/Flush Event Queue|Flush Event Queue]] function. It is not possible to change, destroy or otherwise access the event queue. | Each event structure has an event queue that is managed by LabVIEW. The event queue is processed sequentially by the event structure. It is possible to remove elements from the event queue, using the [[Functions Palette/Programming/Dialog & User Interface/Events/Flush Event Queue|Flush Event Queue]] function. It is not possible to change, destroy or otherwise access the event queue. | ||
=== Event types === | |||
== Event types == | |||
Events are categorized into dynamic and static events. | Events are categorized into dynamic and static events. | ||
==== Dynamic events ==== | |||
=== Dynamic events === | |||
[[File:Event Structure - Dynamic Events - Dynamic Event Terminals.png|thumb|Dynamic Event Terminals on the Event Structure]] | [[File:Event Structure - Dynamic Events - Dynamic Event Terminals.png|thumb|Dynamic Event Terminals on the Event Structure]] | ||
Dynamic events must be registered at runtime using the [[ | Dynamic events must be registered at runtime using the [[Register For Events function|Register For Events]] node, connected to the event structure via the ''Dynamic Event Terminals''. The ''Dynamic Event Terminals'' are hidden by default and must be enabled via the right-click menu option '''Show Dynamic Event Terminals'''. | ||
Registered dynamic events are available in the [[#Edit events|configuration dialog]] under [[#Event sources|event sources]] >> [[#Dynamic|Dynamic]]. | Registered dynamic events are available in the [[#Edit events|configuration dialog]] under [[#Event sources|event sources]] >> [[#Dynamic|Dynamic]]. | ||
==== Static events ==== | |||
=== Static events === | |||
Static events are automatically added to the list of available [[#Event sources|event sources]] and do not have to be registered dynamically. They are generated for the current application, the current VI, panes on the front panel, splitters and controls. Static events are further separated into [[#Notify events|notify events]] and [[#Filter events|filter events]]. | Static events are automatically added to the list of available [[#Event sources|event sources]] and do not have to be registered dynamically. They are generated for the current application, the current VI, panes on the front panel, splitters and controls. Static events are further separated into [[#Notify events|notify events]] and [[#Filter events|filter events]]. | ||
===== [[File:Event Structure - Notify Event.png|frameless|border|Notify event]] Notify events ===== | |||
==== [[File:Event Structure - Notify Event.png|frameless|border|Notify event]] Notify events ==== | |||
Notify events handle a specific event. They are represented in the [[#Edit events|configuration dialog]] by a green arrow: [[File:Event Structure - Notify Event.png|frameless|border|Notify event]] | Notify events handle a specific event. They are represented in the [[#Edit events|configuration dialog]] by a green arrow: [[File:Event Structure - Notify Event.png|frameless|border|Notify event]] | ||
===== [[File:Event Structure - Filter Event.png|frameless|border|Filter event]] Filter events ===== | |||
==== [[File:Event Structure - Filter Event.png|frameless|border|Filter event]] Filter events ==== | |||
[[File:Event Structure - Event Filter Node.png|thumb|Event Filter Node on the Event Structure]] | [[File:Event Structure - Event Filter Node.png|thumb|Event Filter Node on the Event Structure]] | ||
| Line 39: | Line 35: | ||
Filter events are executed '''before''' the actual event happens and have an additional '''filter node''' on the subdiagram. The '''filter node''' makes it possible to dynamically ''filter'' (and in some cases even ''alter'') notify events. Filter events are represented in the [[#Edit events|configuration dialog]] by a red arrow: [[File:Event Structure - Filter Event.png|frameless|border|Filter event]] | Filter events are executed '''before''' the actual event happens and have an additional '''filter node''' on the subdiagram. The '''filter node''' makes it possible to dynamically ''filter'' (and in some cases even ''alter'') notify events. Filter events are represented in the [[#Edit events|configuration dialog]] by a red arrow: [[File:Event Structure - Filter Event.png|frameless|border|Filter event]] | ||
=== Timeout behavior === | |||
== Timeout behavior == | |||
The timeout terminal on the event structure allows to execute the '''Timeout''' event if no other event has been executed for a certain amount of time. The event structure waits indefinitely if no value is connected to the timeout terminal or if the value is set to a value less than zero. If the timeout is set to a value greater than or equal to zero, the '''Timeout''' event is executed if no other event is executed within the specified period. | The timeout terminal on the event structure allows to execute the '''Timeout''' event if no other event has been executed for a certain amount of time. The event structure waits indefinitely if no value is connected to the timeout terminal or if the value is set to a value less than zero. If the timeout is set to a value greater than or equal to zero, the '''Timeout''' event is executed if no other event is executed within the specified period. | ||
=== Edit events === | |||
== Edit events == | |||
[[File:Event Structure - Edit Events Dialog.png|thumb|Configuration dialog for event structures (Edit Events)]] | [[File:Event Structure - Edit Events Dialog.png|thumb|Configuration dialog for event structures (Edit Events)]] | ||
| Line 72: | Line 64: | ||
The dialog is split into three columns: [[#Event specifiers|Event specifiers]], [[#Event sources|event sources]] and [[#Events|events]]. | The dialog is split into three columns: [[#Event specifiers|Event specifiers]], [[#Event sources|event sources]] and [[#Events|events]]. | ||
=== Event specifiers === | === Event specifiers === | ||
| Line 79: | Line 70: | ||
Lists the event sources and events for the current event case. Each event case can have one or more unique event specifiers. The VI breaks if the same event specifier is used multiple times for the same or different event cases. The '''Add Event''' and '''Remove''' buttons can be used to add or remove events from the list of event specifiers. | Lists the event sources and events for the current event case. Each event case can have one or more unique event specifiers. The VI breaks if the same event specifier is used multiple times for the same or different event cases. The '''Add Event''' and '''Remove''' buttons can be used to add or remove events from the list of event specifiers. | ||
=== Event sources === | === Event sources === | ||
| Line 108: | Line 98: | ||
| Contains the controls and indicators on the front panel of the current VI. [[Cluster|Clusters]] are nested by their containing controls and indicators. | | Contains the controls and indicators on the front panel of the current VI. [[Cluster|Clusters]] are nested by their containing controls and indicators. | ||
|} | |} | ||
=== Events === | === Events === | ||
| Line 132: | Line 120: | ||
This checkbox is ''checked'' by default. When unchecked, any additional events are put on the event queue '''after''' the current event finished executing. | This checkbox is ''checked'' by default. When unchecked, any additional events are put on the event queue '''after''' the current event finished executing. | ||
=== Limit maximum instances of this event in event queue === | === Limit maximum instances of this event in event queue === | ||
| Line 152: | Line 138: | ||
The limit can only be specified if "[[#Lock panel (defer processing of user actions) until the event case completes|Lock panel (defer processing of user actions) until the event case completes]]" is ''unchecked'' (automatically unchecked by LabVIEW). | The limit can only be specified if "[[#Lock panel (defer processing of user actions) until the event case completes|Lock panel (defer processing of user actions) until the event case completes]]" is ''unchecked'' (automatically unchecked by LabVIEW). | ||
< | == Best practice == | ||
* Use the [[Producer/Consumer]] [[:Category:Design patterns|design pattern]] to execute time-consuming tasks outside event structures. This will keep the [[Wikipedia:User interface|user interface]] responsive. | |||
* Use [[Functions Palette/Programming/Dialog & User Interface/Cursor/Set Busy|Set Busy]] and [[Functions Palette/Programming/Dialog & User Interface/Cursor/Unset Busy|Unset Busy]] when executing long-running events to give the user a visual feedback. | |||
* Use only one event structure in a [[Functions Palette/Programming/Structures/While Loop|while loop]]. | |||
* '''Never''' handle the same event in multiple event structures. | |||
* '''Never''' place an event structure within another event structure. | |||
== FAQ == | |||
=== Why doesn't the event structure register local variable changes? === | |||
This is a design choice. Local variables are often used inside an event structure to update values on the front panel. If an event updates the value of the same control that generated the event, it would result in an infinite loop if the event is also generated for local variables. To programmatically generate events for controls use a [[Property node|property node]] for the '''Value (Signaling)''' property.<ref>https://knowledge.ni.com/KnowledgeArticleDetails?id=kA00Z0000019N6xSAE</ref> | |||
== History == | == History == | ||
| Line 159: | Line 157: | ||
! Version | ! Version | ||
! Change(s) | ! Change(s) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:LV8-2013.png|frameless|border|64x64px|LabVIEW 2013|link=LabVIEW 2013]] | | [[File:LV8-2013.png|frameless|border|64x64px|LabVIEW 2013|link=LabVIEW 2013]] | ||
| | | In [[LabVIEW 2013]] unhandled, dynamically registered events do not reset the timeout. Previously, if a dynamic event was registered but there was not an event case in the structure for the event, if the event fired the timeout would still be reset. In [[LabVIEW 2013]] and later if there is not an event case in the structure for the event even if registered then it will not cause the timeout to reset. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:LV8-2013.png|frameless|border|64x64px|LabVIEW 2011|link=LabVIEW 2011]] | | [[File:LV8-2013.png|frameless|border|64x64px|LabVIEW 2011|link=LabVIEW 2011]] | ||
| | | In [[LabVIEW 2011]] The Value Change is the default event when you define a new event case for a control or indicator. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[File:LV7.png|frameless|border|64x64px|LabVIEW 6.1|link=LabVIEW 6i]] | | [[File:LV7.png|frameless|border|64x64px|LabVIEW 6.1|link=LabVIEW 6i]] | ||
| | | The Event Structure was added in [[LabVIEW 6i]]. Prior to this version, Event-Driven Programming was not supported. | ||
|} | |} | ||
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Revision as of 20:18, 23 June 2020
| Object information | |
|---|---|
| Owning palette(s) | Structures palette | Events palette |
| Type | Structure |
| Requires | Basic Development Environment |
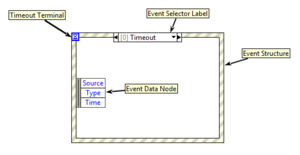
An Event Structure is a primitive structure that can have multiple subdiagrams (also known as "Event cases"), one of which is selectively executed at runtime. The structure waits for an event to occur, or until the timeout elapsed. While it waits, it doesn't take up any CPU time. Events can be triggered by user input or programmatically by the software. If an event happens while another event is executing, the new event is put on the event queue.
Usage
The event queue
Each event structure has an event queue that is managed by LabVIEW. The event queue is processed sequentially by the event structure. It is possible to remove elements from the event queue, using the Flush Event Queue function. It is not possible to change, destroy or otherwise access the event queue.
Event types
Events are categorized into dynamic and static events.
Dynamic events
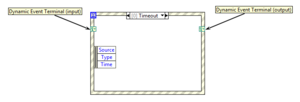
Dynamic events must be registered at runtime using the Register For Events node, connected to the event structure via the Dynamic Event Terminals. The Dynamic Event Terminals are hidden by default and must be enabled via the right-click menu option Show Dynamic Event Terminals.
Registered dynamic events are available in the configuration dialog under event sources >> Dynamic.
Static events
Static events are automatically added to the list of available event sources and do not have to be registered dynamically. They are generated for the current application, the current VI, panes on the front panel, splitters and controls. Static events are further separated into notify events and filter events.
 Notify events
Notify events
Notify events handle a specific event. They are represented in the configuration dialog by a green arrow: ![]()
 Filter events
Filter events
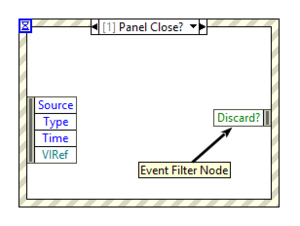
Filter events are executed before the actual event happens and have an additional filter node on the subdiagram. The filter node makes it possible to dynamically filter (and in some cases even alter) notify events. Filter events are represented in the configuration dialog by a red arrow: ![]()
Timeout behavior
The timeout terminal on the event structure allows to execute the Timeout event if no other event has been executed for a certain amount of time. The event structure waits indefinitely if no value is connected to the timeout terminal or if the value is set to a value less than zero. If the timeout is set to a value greater than or equal to zero, the Timeout event is executed if no other event is executed within the specified period.
Edit events
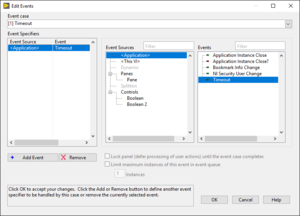
Events can be configured via the right-click menu options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Edit Events Handled by This Case... | Opens the configuration dialog for the current event case. |
| Add Event Case... | Adds a new event case to the structure and opens the configuration dialog. |
| Duplicate Event Case... | Makes a copy of the currently selected event in a new event case and opens the configuration dialog. |
| Delete This Event Case | Deletes the currently selected event case. |
The dialog is split into three columns: Event specifiers, event sources and events.
Event specifiers
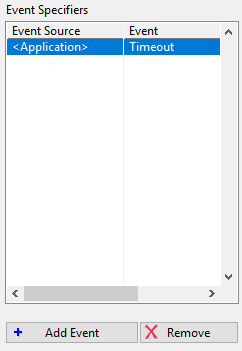
Lists the event sources and events for the current event case. Each event case can have one or more unique event specifiers. The VI breaks if the same event specifier is used multiple times for the same or different event cases. The Add Event and Remove buttons can be used to add or remove events from the list of event specifiers.
Event sources
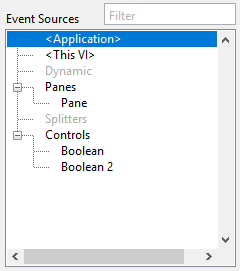
Lists the event sources for the current VI. Categories in angle brackets are fixed and always available for all VIs. Grayed-out categories have no event sources.
| Event source | Description |
|---|---|
| <Application> | Events for the current application instance (executable) |
| <This VI> | Events for the current VI |
| Dynamic | Contains dynamic events registered by the dynamic events terminal |
| Panes | Contains entries for panels on the front panel (by default only "Pane") |
| Splitters | Contains entries for splitters on the front panel of the current VI |
| Controls | Contains the controls and indicators on the front panel of the current VI. Clusters are nested by their containing controls and indicators. |
Events
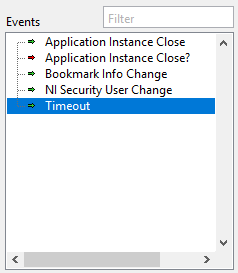
Lists notify and filter events for the currently selected event source. The filter box can be used to search for specific events. The description for each event is available in the help window while hovering over an entry in the list.
Lock panel (defer processing of user actions) until the event case completes
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| The front panel is unresponsive to user input while the event case executes. | |
| The front panel stays responsive to user input while the event case executes. |
This checkbox is checked by default. When unchecked, any additional events are put on the event queue after the current event finished executing.
Limit maximum instances of this event in event queue
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| The maximum number of events in the event queue for the current event case is limited to the specified number of instances. | |
| The number of events in the event queue is unlimited. |
This checkbox is unchecked by default. When checked, the maximum number of events for the current event case can be defined in the Instances control below the checkbox.
The limit can only be specified if "Lock panel (defer processing of user actions) until the event case completes" is unchecked (automatically unchecked by LabVIEW).
Best practice
- Use the Producer/Consumer design pattern to execute time-consuming tasks outside event structures. This will keep the user interface responsive.
- Use Set Busy and Unset Busy when executing long-running events to give the user a visual feedback.
- Use only one event structure in a while loop.
- Never handle the same event in multiple event structures.
- Never place an event structure within another event structure.
FAQ
Why doesn't the event structure register local variable changes?
This is a design choice. Local variables are often used inside an event structure to update values on the front panel. If an event updates the value of the same control that generated the event, it would result in an infinite loop if the event is also generated for local variables. To programmatically generate events for controls use a property node for the Value (Signaling) property.[1]
History
| Version | Change(s) |
|---|---|

|
In LabVIEW 2013 unhandled, dynamically registered events do not reset the timeout. Previously, if a dynamic event was registered but there was not an event case in the structure for the event, if the event fired the timeout would still be reset. In LabVIEW 2013 and later if there is not an event case in the structure for the event even if registered then it will not cause the timeout to reset. |

|
In LabVIEW 2011 The Value Change is the default event when you define a new event case for a control or indicator. |

|
The Event Structure was added in LabVIEW 6i. Prior to this version, Event-Driven Programming was not supported. |
See also
External links
- National Instruments: Event-Driven Programming in LabVIEW
- National Instruments: Caveats and Recommendations when Using Events in LabVIEW
