Reshape Array function: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Add content |
Clarify best practice for Array Subset |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
== Best practice == | == Best practice == | ||
* If the input and output dimensionality is the same, use [[Array Subset function|Array Subset]] instead. | * If the input and output dimensionality is the same but with less elements, use [[Array Subset function|Array Subset]] instead. | ||
* To swap the dimensionality of 2D arrays (<code>[i:j]</code> to <code>[j:i]</code>), use [[Transpose 2D Array function|Transpose 2D Array]] instead. | * To swap the dimensionality of 2D arrays (<code>[i:j]</code> to <code>[j:i]</code>), use [[Transpose 2D Array function|Transpose 2D Array]] instead. | ||
[[Category:Array Palette]] | [[Category:Array Palette]] | ||
Revision as of 21:14, 15 November 2019
| Object information | |
|---|---|
| Owning palette(s) | Array palette |
| Type | Function |
| Requires | Basic Development Environment |
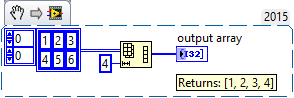
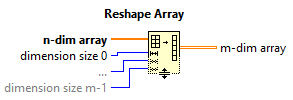
The Reshape Array function takes an array of any size and dimensionality and turns it into an array of different dimensionality using the original elements.
Usage
Connect an array of any size and dimensionality to n-dim array and extend the bottom border of the function until the desired number of output dimensions is reached. For each dimension specify the maximum number of elements. The resulting array contains exactly the desired number of elements.
|
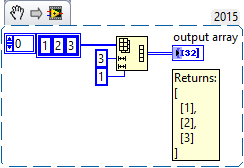
|
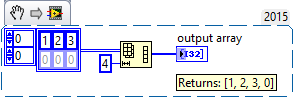
If the source contains more elements than desired, the array is cut off.
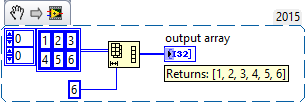
If the source array contains less elements than desired, the array is padded with zeros.
Best practice
- If the input and output dimensionality is the same but with less elements, use Array Subset instead.
- To swap the dimensionality of 2D arrays (
[i:j]to[j:i]), use Transpose 2D Array instead.