Rotate 1D Array function: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Add new page (stub) |
Add content |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Rotate 1D Array - Terminals.png|thumb|Rotate 1D Array function]] | [[File:Rotate 1D Array - Terminals.png|thumb|Rotate 1D Array function]] | ||
{{LabVIEW Palette Object Information|palette=Functions Palette/Programming/Array{{!}}Array palette|type=function}} | {{LabVIEW Palette Object Information|palette=Functions Palette/Programming/Array{{!}}Array palette|type=function}} | ||
The '''Rotate 1D Array''' function takes a one-dimensional array and moves the start of the array by the number of elements specified, effectively "rotating" the array. | |||
== Usage == | == Usage == | ||
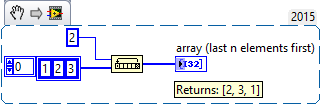
Connect a one-dimensional array at the '''array''' input terminal and specify the number of elements to move at '''n'''. The resulting array will contain all elements from the source array "rotated" by the number of elements specified. | |||
[[File:Rotate 1D Array - Rotate Right.png]] | |||
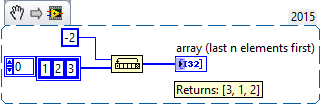
It is also possible to specify a negative value for '''n''' to "rotate" in the opposite direction. | |||
[[File:Rotate 1D Array - Rotate Left.png]] | |||
A value of zero results in a <u>[[Wikipedia:NOP_(code)|no-op]]</u> which leaves the original array unchanged. | |||
[[File:Rotate 1D Array - No-op.png]] | |||
[[Category:Array Palette]] | [[Category:Array Palette]] | ||
Revision as of 17:56, 18 November 2019

| Object information | |
|---|---|
| Owning palette(s) | Array palette |
| Type | Function |
| Requires | Basic Development Environment |
The Rotate 1D Array function takes a one-dimensional array and moves the start of the array by the number of elements specified, effectively "rotating" the array.
Usage
Connect a one-dimensional array at the array input terminal and specify the number of elements to move at n. The resulting array will contain all elements from the source array "rotated" by the number of elements specified.
It is also possible to specify a negative value for n to "rotate" in the opposite direction.
A value of zero results in a no-op which leaves the original array unchanged.